Enterprise PKI: Securing Digital Identities in Organizations
Enterprise PKI: Securing Digital Identities in Organizations
Blog Article
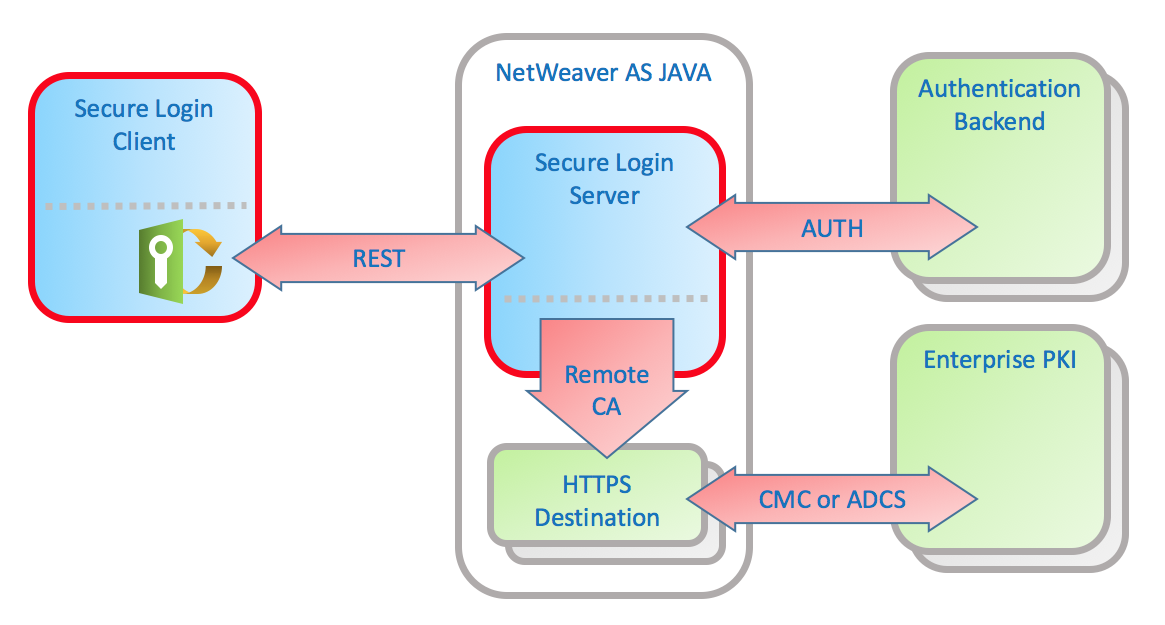
Enterprise Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a framework of policies, processes, and technologies that enables secure authentication, encryption, and digital signatures within an organization. It helps enterprises manage digital certificates, ensuring secure communication and access control across various systems and applications. This article explores the key components, benefits, and best practices of Enterprise PKI.
Understanding Enterprise PKI
Enterprise PKI is a centralized solution that provides digital certificates for securing internal and external communications. It enables organizations to establish trust, protect sensitive data, and meet compliance requirements by leveraging cryptographic key pairs for authentication and encryption.
Key Components of Enterprise PKI
1. Certificate Authority (CA)
- The CA is responsible for issuing, renewing, and revoking digital certificates.
- Can be an internal CA managed by the enterprise or an external trusted CA.
2. Registration Authority (RA)
- Verifies and approves certificate requests before they are issued by the CA.
- Helps enforce identity verification policies.
3. Certificate Repository
- A secure database where issued certificates and revocation lists are stored.
- Can be integrated with enterprise directory services.
4. Certificate Revocation List (CRL) & Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)
- CRL maintains a list of revoked certificates to prevent unauthorized use.
- OCSP provides real-time certificate status verification.
5. Secure Key Management
- Protects private keys using Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) or secure storage solutions.
- Ensures keys are generated, stored, and used securely.
Benefits of Enterprise PKI
- Enhanced Security: Provides strong encryption and authentication mechanisms.
- Centralized Identity Management: Simplifies certificate issuance and tracking within an organization.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps meet security standards such as ISO 27001, NIST, and GDPR.
- Scalability: Supports thousands of users, devices, and applications in a large enterprise.
- Automated Certificate Management: Reduces the risk of expired or misconfigured certificates.
Best Practices for Enterprise PKI Implementation
- Use a Hierarchical PKI Structure: Implement a multi-tier architecture with root and subordinate CAs for better security.
- Secure Private Keys: Store private keys in HSMs to prevent unauthorized access.
- Automate Certificate Lifecycle Management: Use certificate management tools to monitor, renew, and revoke certificates efficiently.
- Enforce Strong Authentication Policies: Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for certificate issuance and access.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic assessments to identify vulnerabilities and maintain compliance.
Applications of Enterprise PKI
- Secure Email Communication: Encrypts and signs corporate emails to prevent phishing and tampering.
- User and Device Authentication: Enables secure access to corporate networks and applications.
- SSL/TLS Certificates for Websites and Services: Ensures encrypted communication between users and enterprise systems.
- Code Signing: Verifies software authenticity and integrity before execution.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Security: Protects connected devices with unique digital identities.
Conclusion
Enterprise PKI is a critical security infrastructure that enables organizations to safeguard digital identities, secure communications, and meet compliance requirements. By implementing robust PKI policies and automating certificate management, enterprises can enhance security, streamline operations, and build a trusted digital ecosystem. Report this page